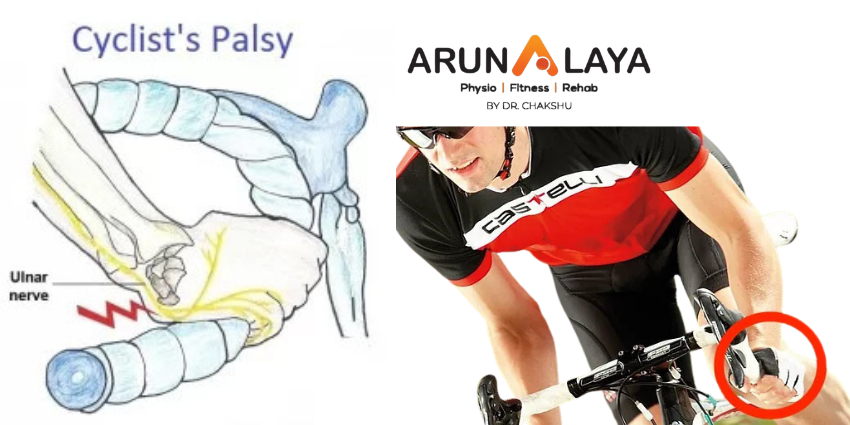
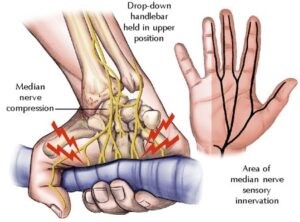
Tendon Neuroplastic Training: A Game-Changer in Tendonitis Rehab
Introduction:
Neuroplasticity, the phenomenon of altering neuronal connections in response to various stimuli, plays a vital role in the body’s ability to adapt, learn, and recover from injuries. When it comes to tendonitis, a condition that affects tendons in both upper and lower limbs, the concept of Tendon Neuroplastic Training is revolutionizing rehabilitation. In this article, we explore what Tendon Neuroplastic Training entails and how physiotherapy can enhance its effectiveness.
Understanding Tendonitis and Its Rehabilitation Challenges:
Tendonitis can impact tendons in various areas of the body, such as tennis elbow, golfer’s elbow, patellar tendonitis, Achilles tendonitis, and high hamstring tendonitis. Although exercise therapy has traditionally been the primary approach to alleviate tendonitis pain, returning to sports activities can be a struggle. The challenge lies in not only strengthening the muscles but also optimizing motor control, the ability to contract muscles smoothly.
Introducing Tendon Neuroplastic Training:
Tendon Neuroplastic Training is a groundbreaking approach that shifts the focus from merely targeting the tendons and muscles to directly engaging the nervous system. This innovative concept transforms how individuals perform strengthening exercises, retraining the brain and body to enhance the overall effectiveness of tendonitis rehab.
Tendons Suited for Tendon Neuroplastic Training:
This unique training methodology is suitable for most lower limb tendons, including Achilles, patellar, and hamstring origin tendons. Additionally, it can be applied to upper limb tendons affected by conditions like tennis or golfer’s elbow. To determine the suitability of Tendon Neuroplastic Training for your specific case, it is advisable to consult with a knowledgeable physiotherapist or sports doctor.
The Role of Physiotherapy in Tendon Neuroplastic Training:
Physiotherapy plays a pivotal role in implementing and optimizing Tendon Neuroplastic Training. Here’s how physiotherapists contribute to this innovative approach:
- Assessment: Physiotherapists conduct a comprehensive assessment to identify the specific tendonitis issues and the areas that require attention.
- Customized Training: Based on the assessment findings, physiotherapists create a tailored Tendon Neuroplastic Training program that addresses the individual’s unique needs and goals.
- Guidance and Feedback: Physiotherapists guide patients through the training process, ensuring they understand and perform exercises correctly. They provide ongoing feedback and adjustments as needed.
- Motor Control Enhancement: Physiotherapists focus on improving motor control by incorporating metronome training into the program. This method helps individuals contract their muscles smoothly and enhances the success of tendonitis rehabilitation.
Conclusion:
Tendon Neuroplastic Training is a game-changer in the realm of tendonitis rehabilitation, offering a novel approach that targets the nervous system to enhance results. With the guidance and expertise of physiotherapists, individuals can harness the power of neuroplasticity to recover more effectively from tendonitis, improving both muscle strength and motor control. This innovative combination empowers patients to return to their sports and activities with confidence and reduced pain.