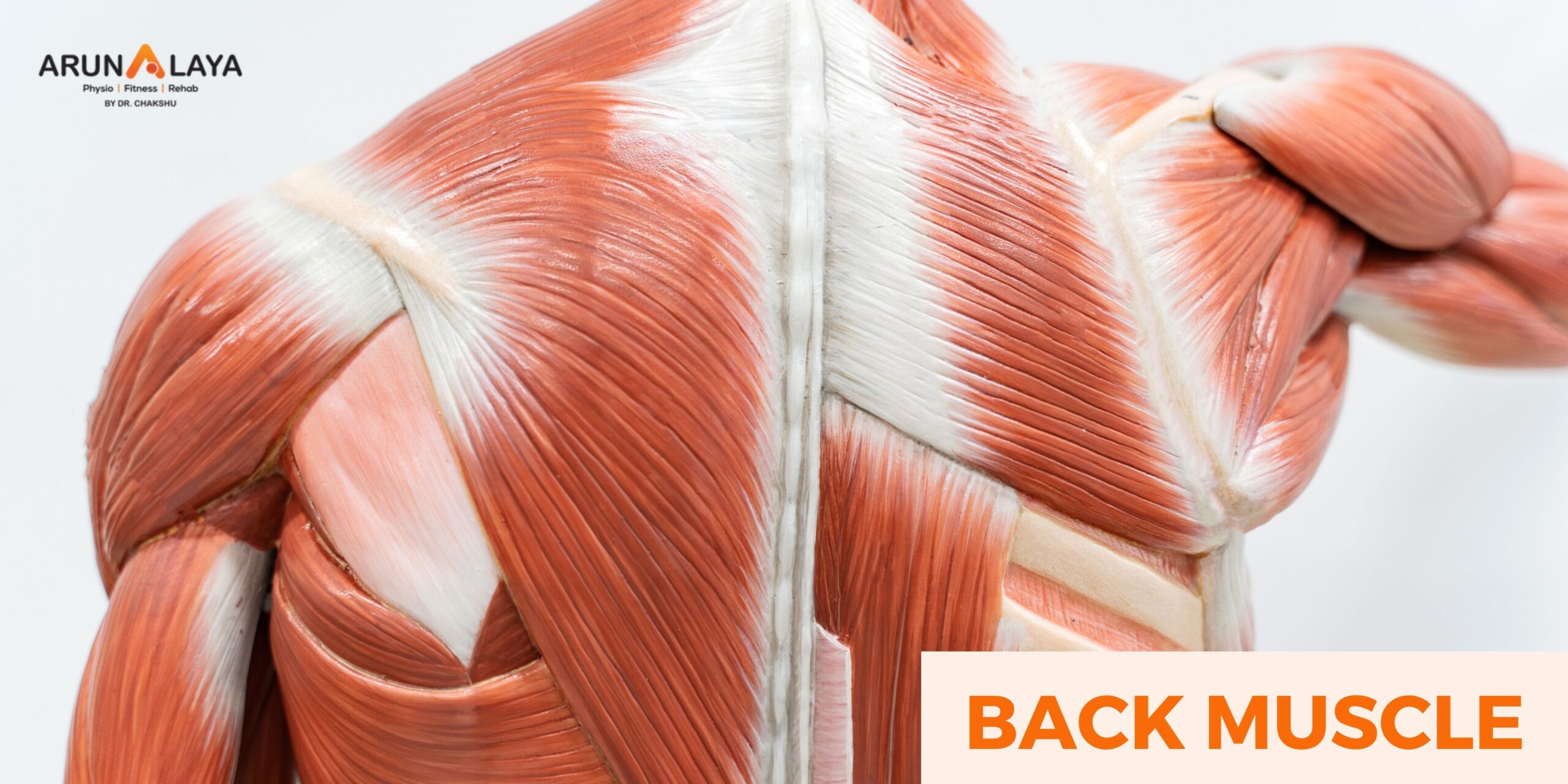
The Impact of Sitting on Back Muscles and How to Sit Better for Spinal Health
Introduction: The way we sit significantly affects the health of our back muscles and our overall spinal well-being. When we’re in motion, the flexibility of our spine allows it to contract and expand, acting as a natural shock absorber for our vertebrae. But sitting for prolonged periods puts extra pressure on the spine, compressing our spinal discs and reducing spinal flexibility. This article explores the consequences of prolonged sitting on our back muscles and provides simple tips for healthier sitting habits.
The Impact of Sitting on Our Spine:
- Increased Pressure on Discs:
- Prolonged sitting increases pressure on the spine, leading to the compression of spinal discs. This can reduce the flexibility of the spine and increase the likelihood of conditions like herniated discs, back muscle weakness, and a higher risk of injury.
- Weakened Back Muscles:
- Frequent sitting can result in weakened core and back muscles, which are vital for supporting the spine. Weak muscles offer inadequate support and can lead to postural issues and back pain.
- Tightened Hip Flexors:
- Sitting for extended periods tightens the hip flexor muscles. These tight muscles can restrict blood flow to the gluteal muscles, another set of essential muscles that support the spine.
- Postural Effects:
- Sitting often leads to rounded shoulders and a forward head posture. Such poor posture can cause spinal ligaments to stretch, accelerating disc wear and tear.
How to Sit Better for Spinal Health:
- Adjust Chair Height:
- Modify the height of your chair to ensure it aligns with your desk. Proper chair height promotes better posture and spinal alignment.
- Consider Ergonomic Mouse and Keyboard Position:
- Pay attention to the placement of your mouse and keyboard. Keep them at an ergonomically friendly distance to support your wrists and minimize strain.
- Optimal Monitor Position:
- Position your monitor or screen directly in front of you at a comfortable height and distance. Avoid twisting or looking downward to see your screen.
- Take Regular Breaks:
- For the sake of your spine and overall health, take short breaks when sitting for extended periods. Even a brief stand-up break can help alleviate the strain on your back and encourage spinal mobility.
Conclusion: Prolonged sitting can take a toll on your back muscles and spinal health, resulting in issues such as weakened muscles, spinal compression, and poor posture. Fortunately, adopting better sitting habits can significantly improve your spinal well-being. By making simple adjustments to your chair, input devices, and monitor, and by taking regular breaks, you can minimize the negative impact of sitting, promoting a healthier and more comfortable sitting experience while safeguarding your back muscles and spine.